Needle Free Covid Vaccine?
In the countries of India and China, there are two alternative ways to receive a Covid vaccine: an inhale through the mouth or a squirt in the nose. According to Jamaica Hospital, around 10% of the human population is afraid of needles. As reported by the CDC, “As many as 1 in 10 people might delay the COVID-19 vaccine due to these fears.” Trypanophobia is the fear of needles, a common fear that impacts one’s decisions regarding their health. These new needle-free approaches may boost the number of people that are receiving the vaccine, especially targeting those who cannot take injections due to various reasons.
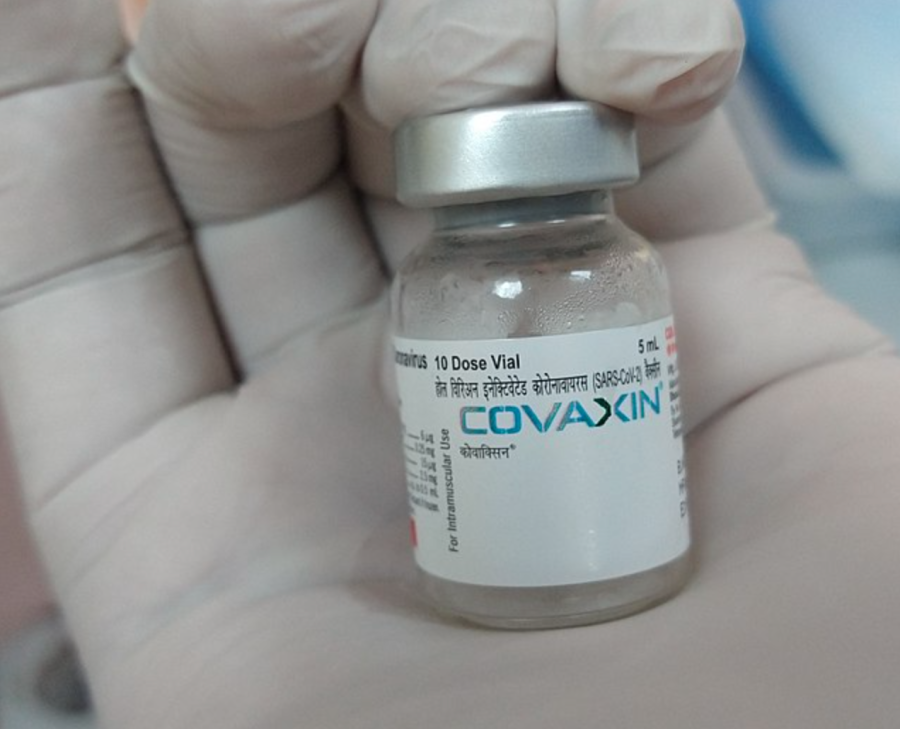
In India, Bharat Biotech created a nasal vaccine that was approved by regulators in early September 2022. Also known as iNCOVACC, they have recently finished trials to get their vaccine approved. According to the Washington University School of Medicine, researchers who worked with Bharat to develop the vaccine included a Phase 3 trial with about 3,100 previously unvaccinated individuals; they were test subjects that got two doses of the nasal vaccine. Another booster trial was also held with 875 individuals who received all three doses. Trials revealed that the vaccination elicited a potent immune response, but they also failed to document whether it lessened symptoms of the disease. However, the findings have not yet been made public or subjected to peer review.
CanSino Biologics, a company based in China, also had their nasal vaccine approved recently by the National Medical Products Administration of China for Convidecia Air. Some scientists argue that this sort of breakthrough is extremely diligent in the sense that more people would be willing to get vaccinated. “It’s important and definitely exciting to see how the data turns out in terms of its effectiveness.” says professor and clinical virologist Siddharth Sridhar. As of late September 2022, CanSino Biologics has completed phase 1 and phase 2 for the process of approval; the earliest human studies of a novel medicine are typically called phase I investigations. Finding the maximum dose of the novel medication that can be administered safely without having serious side effects is the goal of phase I research. The first phase consisted of 130 people, and the results are already out. According to The Wall Street Journal, “two doses of the vaccine generated an antibody response similar to one dose of an injected vaccine.” Similarly to the covid injection vaccine, two doses must be administered.
These new innovative inventions have sparked skepticism and controversy about how effective they genuinely are. According to Nature Journal, they proclaim that there is a lack of evidence that can determine the effectiveness of these nasal approaches. Their article states, “Vaccines inhaled through the mouth or nose might stop the coronavirus in its tracks, although there’s little evidence from human trials so far.” On the other hand, some contend that these alternatives would boost the number of people willing to get vaccinated. According to The National Center of Biotechnology Information Company, “fear of needles and of pain after vaccination is also a documented barrier to vaccination.” At the end of the day, it is up to the user to determine whether or not they are willing to receive these alternatives.
Although Asia is the first to undergo two new needle-free approaches to getting the Covid vaccine, they are quickly coming into existence despite the alternatives being far less studied than the original injected options.